RN – Reproductive Health (Contraceptive Management) Certified
Selected Care Activities 0/0
Additional Care Activities this role could do
Care Activities this role could do
Controls on Nursing Practice
There are 4 levels of control on practice for nurses. Controls at level 3 and 4 are important to consider when hiring a nurse into primary care.
Organizations and employers (YOU!) are responsible for providing support, training, clinical policies specific to your clinic, and workflow processes to support nurses in practice. Employers/Clinics can also place employer or organization level controls on practice for nurses but you cannot expand the nursing scope of practice beyond what provincial legislation allows.
Additionally, each Individual nurse will have their own competency. Each nurse is legally and professionally responsible for their own autonomous nursing practice. Nurses are responsible for assessing their individual competency. Although a care activity may be set out by BCCNM as part of a scope of practice, an individual nurse may determine that they do not have a competency or have been unable to maintain a competency.
Nurses are responsible for communicating their scope and limits to their employer and actively working with their employer to maintain competency in areas of mutually identified relevance. Nurses and employers work together to identify opportunities for developing competencies to meet the needs of patients. Clinic leaders and colleagues must respect individual nursing competency. If an individual nurse says “no”, a clinic employer or fellow clinician colleague can’t say “yes”.
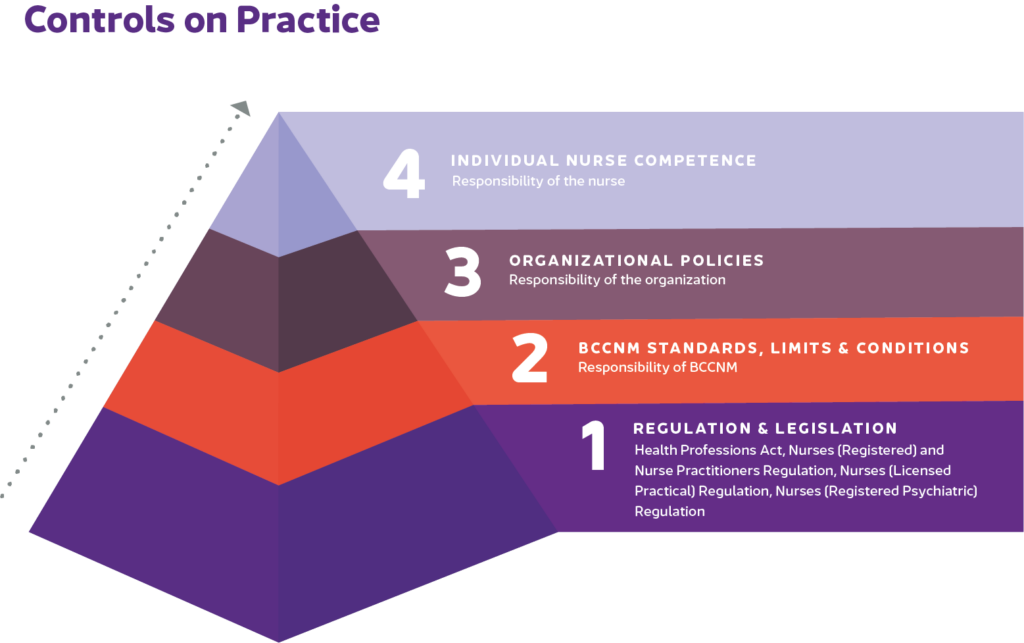
From Controls on Nursing Practice, by British Columbia College of Nurses and Midwives. Reprinted with permission.